Parts of Speech
In the English language words are grouped into different categories called Parts of Speech. There are 9 Parts of Speech in the English.
Noun

Definition of a Noun
- A noun is a word that describes a person, place or thing.
- Nouns give a name to a word.
- There are 2 main types of nouns, common nouns and proper nouns.
- Nouns are one of the 9 Parts of Speech in the English language.
Types of Nouns
1. Common noun with examples
- A common noun is a person, place or thing that is a general object, not a specific object.
- A common noun names an object or thing like a book, or names a place like a forest or a mall.
- Common nouns are only capitalized when it starts a sentence.
2. Proper noun with examples
- A proper noun is a person, place or thing that is a specific object, not a general object.
- A proper noun names people for example Sally, or a specific name we give to a place like England, or a specific name of a company like Apple, or Mc Donald’s.
- Proper nouns are always capitalized.

Other Types of Nouns with Examples

Countable Noun
A countable noun is a noun you can count using numbers.
E.g. 5 fingers, 2 dogs, 5 bags.
How many fingers do you see?

Uncountable Noun
An uncountable noun is a noun you can not count.
E.g. water, hair, love
Can I please have some water?

Concrete Noun
A concrete noun you experience with your senses.
E.g. You can see, hear, taste or smell it
Think about your favourite food.

Collective Noun
A collective noun represents a group of people, animals or things.
E.g. A group of fish is called a school of fish.
E.g. Many players in a group is called a team.

Abstract Noun
An abstract noun is an idea, feeling, or state of being.
E.g. Love, surprise, happiness
Think about your emotions and how you feel.

Possessive Noun
A possessive noun shows ownership with ‘s or s’.
E.g. That is Jack’s bag. (singular possessive noun)
E.g. Those are the boys’ bags. (plural possessive noun)
Verb

Definition of a Verb
- A verb is a word that describes what the subject is doing.
- A verb either describes an action, E.g. The girl eats ice-cream.
- Or a verb can describe a feeling (state of being). E.g. She feels sleepy.
- Verbs are one of the 9 Parts of Speech in the English language.
Types of Verbs
1. Dynamic Verb with examples
- A Dynamic verb describes a physical action, and can also be called an action verb.
- E.g. The boy jumps. Or E.g. The woman talks.
- A dynamic verb lets you know what the subject is doing.
2. Stative Verb with examples
- We use Stative verb to describe a state of being, not a physical action.
- E.g. I believe you are correct.
- We mostly use Stative verbs to express what we think and feel.
- Careful! Some words can be both dynamic and stative.
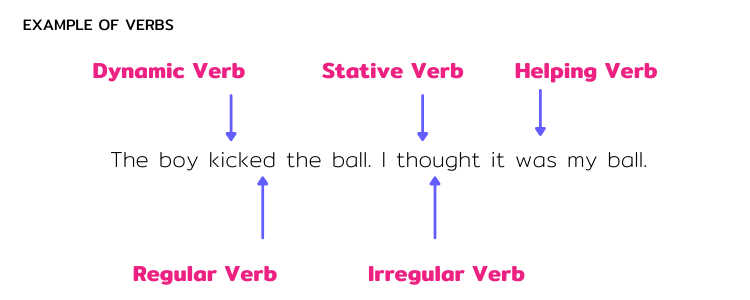
Other Types of Verbs with Examples

Helping Verb
Helping verbs help the main verb in tenses to make sense.
E.g. He a man = He is a man.
Some people call it an auxillary verb.

Modal Verb
A Modal verb changes the meaning of the main verb slightly.
Use modals to suggest, ask permission, be polite etc.
E.g. You should go to bed.

Regular Verb
In English tenses Regular verbs end with -ed / -d.
Used in the “simple past tense”.
E.g. Sally walked to school.

Linking Verb
A linking verb links the subject with a word (adjective),
that gives information about the subject.
E.g. Jenny felt sleepy after dinner.

Irregular Verb
Irregular Verbs don’t end with -ed / -d.
The verb can change if it’s Verb 1, Verb 2, or Verb 3.
E.g. Eat / ate / eaten. Jimmy ate candy all day.

Phrasal Verb
When you use a verb and preposition together it’s called a phrasal verb.
E.g. Get in the car.
Here “get in” is the phrasal verb.
Adjective

Definition of an Adjective
- An adjective describes a noun. So it gives more information about a person, place, or thing.
- For example, “He has hairy legs”. The word “hairy” describes how the leg looks.
- Adjectives can also compare, show possession, act as a participal, restrict, and describe features of a noun.
- Adjectives are one of the 9 Parts of Speech in the English language.
Types of Adjectives
1. Descriptive Adjective with examples
- A descriptive adjective describes or adds meaning to nouns and pronouns.
- It is the most used type of adjective.
- For example, “He told a joke.” Is a joke always funnny? No. He could have told a “bad” joke too.
2. Proper Adjective with examples
- A proper adjective is an adjective that is capitalized (c = C) and comes from a Proper Noun.
- E.g. This is a Shakespearean poem. (Person Proper Noun = Shakespeare)
- E.g. That is the American flag. (Place Proper Noun = America)

Other Types of Adjectives with Examples

Comparative Adjectives
A comparative adjective compared two things.
E.g. The boy is taller than the girl.
E.g. The red pen is more expensive than the blue pen.

Superlative Adjectives
A superlative adjective compares more that two things.
E.g. That is the tallest building in town.
E.g. The girl is the smartest in the class.

Possessive Adjectives
A possessive adjective shows ownership and comes before the noun. It is similar to a possessive pronoun but it doesn’t replace the noun.
E.g. This is my ruler.

Interrogative Adjectives
An interrogative adjective begins a question sentence
and is followed by a noun or pronoun.
E.g. What, Which, Whose. “What food do you want?”

Indefinite Adjectives
An indefinite adjective is used to describe a whole group,
and doesn’t point out specific nouns in the group.
E.g. Some of the apples were rotten.

Distributive Adjectives
A distributive adjective refers to individuals in a group.
Example words are, “either, neither, both, each and every”
E.g. Every person in the office will get a bonus.

Attributive Adjectives
An attributive adjective tells us what feature of a noun we’re interested in.
E.g. I love the quiet night.
Here I love the night because it is quite.

Participial Adjectives
A participial adjective is an adjective that acts like a participle.
It usually ends with -ed or -ing and comes from verbs.
E.g. This is an aged book.

Limiting Adjectives
A limiting adjective restricts, instead of describing the noun or pronoun.
E.g. These are your cookies..

Predicate Adjectives
A predicate adjective is an adjective found not next to the noun or pronoun.
E.g Bob is awesome.
Adverb

Definition of an Adverb
- An adverb describes a verb, adjective, phrase or another adverb.
- However, we most often see adverbs describe a verb or adjective.
- An adverb helps to descibe when, how, where, how often or at what degree something happens.
- Adverbs can completely change the meaning of the message so they are a very important.
- Many adverbs end with -ly. Especially adverbs of Frequency and Manner.
- Adverbs are one of 9 Parts of Speech in English grammar.
- There are 5 main types of adverbs.
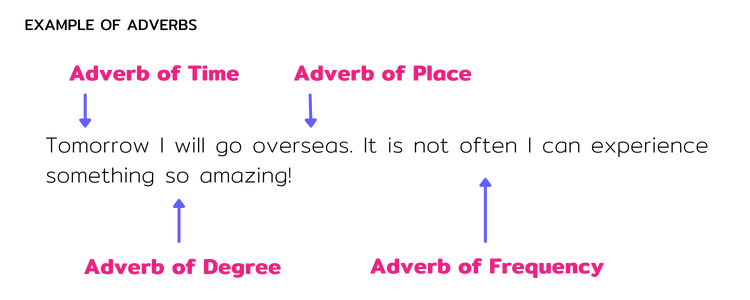
The 5 Types of Adverbs with Examples

Adverbs of Time
Adverbs of time gives information “when” a verb is done.
E.g. Yesterday I went to school.
When did I go to school? Yesterday.

Adverbs of Manner
Adverbs of manner describes how a task was carried out.
E.g. Mark sang loudly in the shower.
How did Mark sing? Loudly!

Adverbs of Place
Adverbs of Place describes “where” a verb is happening.
E.g. It is hot let’s go inside.
Where should we go? Inside.

Adverbs of Frequency
Adverbs of Frequency descibes “how often” a verb is happening.
E.g. I usually go to bed late.
How often do you go to bed late? Usually.

Adverbs of Degree
Adverbs of Degree gives the information “how much” or to what level a verb is done.
E.g. Today is incredibly hot.
To what level do you think it was hot? Incredibly hot!
Pronoun

Definition of a Pronoun
- A pronoun is a word that replaces a noun to avoid repetition.
- The replaced word is either a subject pronoun (I, He, she, they) or an object pronoun (you, it, me).
- The word that is replaced is called the “antecedent”.
- Pronouns are one of the 9 Parts of Speech in the English language.
Types of Pronoun
1. Personal Pronouns with examples
- A personal pronouns replaces people, places or things.
- E.g. I (subject pronoun) really like her (object pronoun).
- E.g. You (subject pronoun) found me (object pronoun)!
2. Possessive Pronouns with examples
- A possessive pronoun shows ownership.
- E.g. The book is his.
- E.g. My friend is late.
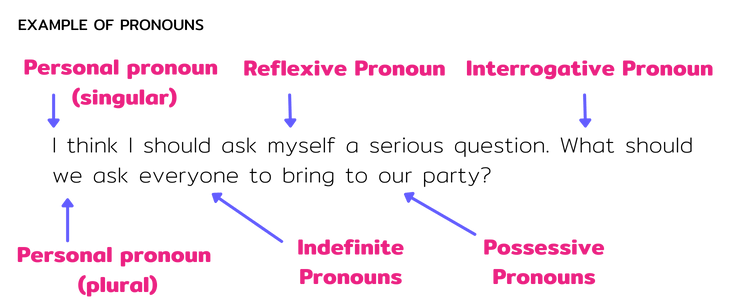
Other Types of Pronouns with Examples

Demonstrative Pronouns
A demonstrative pronoun points at something.
E.g. I like that dress, not this one.
“This” and “That are demonstrative pronouns.

Indefinite Pronouns
An indefinite pronoun makes a non-specific reference.
E.g. Anyone can learn English.
Anyone does not refer to a specific person.

Reflexive Pronouns
A reflexive pronoun is a pronoun that refers back to a person or thing.
These pronouns end with -self / -selves.
E.g. I cannot look at myself.

Relative Pronouns
A relative pronoun relates one part of a sentence with another.
E.g. The man who fell got hurt.
Relative pronouns include, who, whom, when, why, where, whose, that.

Interrogative Pronouns
An interrogative pronoun asks a question.
E.g. What should I do now?
Interrogative pronouns include, What, whom, who.

Reciprocal Pronouns
A receprocal pronoun show mutual action.
E.g. We both like each other.
Receprocal pronouns include, One another, each other.
Preposition

Definition of a Preposition
- A preposition is a small common word that indicates time, location, direction, position and place.
- A simple preposition helps explain the relationship between two or more nouns or pronouns.
- Prepositions usually come before the noun or pronoun, and their purpose it to link the words together.
- Time prepositions include, in, on, at.
- Location prepositions include, at, under, over, by.
- Direction prepositions include, in, into, on, onto.
- A prepositional phrase is a preposition followed by a noun, a pronoun, or another phrase.
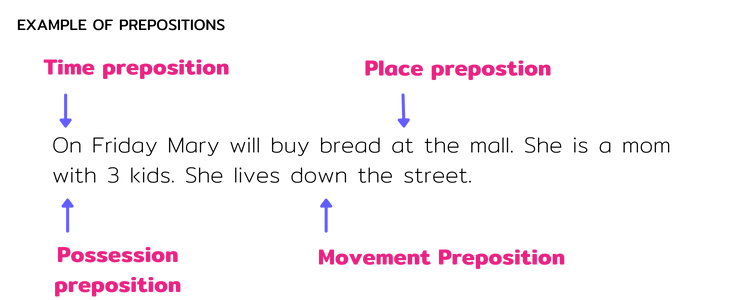
Other Types of Prepositions with Examples

Prepositions of Time
Prepositions of time are:
at – a specific time (e.g. at 6:00am)
on – days (eg. on Friday)
in – months (e.g. in June)

Prepositions of Place
Prepositions of place are:
in – spaces (e.g. in my bag)
on – place (e.g. on the table)
at – specific place (e.g. at the gate)

Prepositions of Movement
Prepositions of movement are:
in, out, around, over, under,
through, up, down, towards, across.
E.g. The boat went under the bridge.

Prepositions of Manner
Prepositions of manner are words that show
the way something happens.
Words like, by, as, in, with.
E.g. She worked as a doctor.

Prepositions of Agent
Prepositions of agent is a thing that is the caused by another thing.
E.g. The song was sang by Elvis.
Here “by” is the agent. We can also use “with”

Prepositions of Measure
Prepositions of measure specifies a value or measurement.
They are the words, By, of, at.
E.g. He was late by 10 minutes.

Prepositions of Possession
Prepositions of possession communicate that
something belongs to a person, animal or thing.
Use the words, Of, In, At, With, On.
E.g. I love a man with a boat.
Conjuctions

Definition of a Conjunction
- Conjuctions link together phrases in a sentence, these can be ideas or actions.
- There are subordinate, coordinating and correlative conjunctions in the English language.
- The different types of conjunctions join different parts of the sentence together.
- Conjunctions are one of the 9 Parts of Speech.

Types of Conjunctions with Examples

Subordinating Conjunctions
A subordinating conjunction links
dependent clauses to independent clauses.
The subordinate clause clarifies the relationship between
the two clauses, to show contrast or cause-and-effect.
Examples conjunctions are; because, since and after.
E.g. I am lonely since we broke up.

Correlative Conjunctions
A correlative conjunction works in pairs to join words together.
The parts in the sentence carry equal importance.
Examples of correlative conjunctions are;
either or, such that / not only, but also
E.g. Not only is she cute, but also smart.

Coordinating Conjunctions
A coordinating conjunction links equal parts of a sentence
such as ; phrases or independent clauses.
A comma (,) joins two independent clauses.
at – specific place (e.g. at the gate)
Examples of coordinating conjunctions;
For, And, Nor, But, Or, Yet, and So.
It’s easy to remember FANBOYS.
E.g. I like chocolate ice-cream, and I like strawberry ice-cream.
Determiner

Definition of a Determiner
- A determiner is a word placed in front of a noun.
- The word can show quantity. E.g 5 fingers.
- Or can show if we are referring to a specific noun or not, by using; a / the.
- Or it can show ownership (possession). E.g. Your wife has lost her keys. (your / her)
- Determiners are one of the 9 Parts of Speech.

Other Types of Determiner with Examples

Article Determiner
Are we referring to a specific noun or not?
An example of an article is; a / an, the.
the = definite article
a/an = indefinite article
E.g. I want to buy a cat. (here I want to buy any cat, not a specific one)
E.g. I want to buy the cat. (here I want to buy a specific cat)

Demonstrative Determiner
A demonstrative determiner gives
information about a noun
and gives us reference if it is close are far away.
An example is; this, that, these, those.
This – something that is close to us.
That – something that is far away.
These – things that are close.
Those – for things that are far away from us.
This and that are singular, and these and those are plural.

Possessive Determiner
Possessive determiners shows possession (or ownership)
of a noun (someone, something, or some place).
An example of a possessive determiner is;
1st person; my / our
2nd person; your
3rd person; his, her, its / their

Quantifier Determiner
Quantifiers tells us (or suggests) the amount of a noun.
An example of a quantifier includes; most, more, some, many, much.
All, every, most, many, some, (a) few, any, no (countable nouns)
much, (a) little, least, most, no (uncountable nouns)
Quantifiers determiners are written in front of an adjective.